- Simple calculation
- Multiple fields for calculation
- Get original field value
- Supported Aggregation Functions
- Batch calculation
- Save and reuse calculated fields
- Language
- Next Steps
Calculated fields are one of the most powerful features for KPI monitoring and prediction. Based on the input data, calculated fields allow you to run statistical functions and create new data items by applying calculations. As Trendz Analytics processes the calculations on the fly, no data from ThingsBoard database will be damage. And no additional load will be applied.
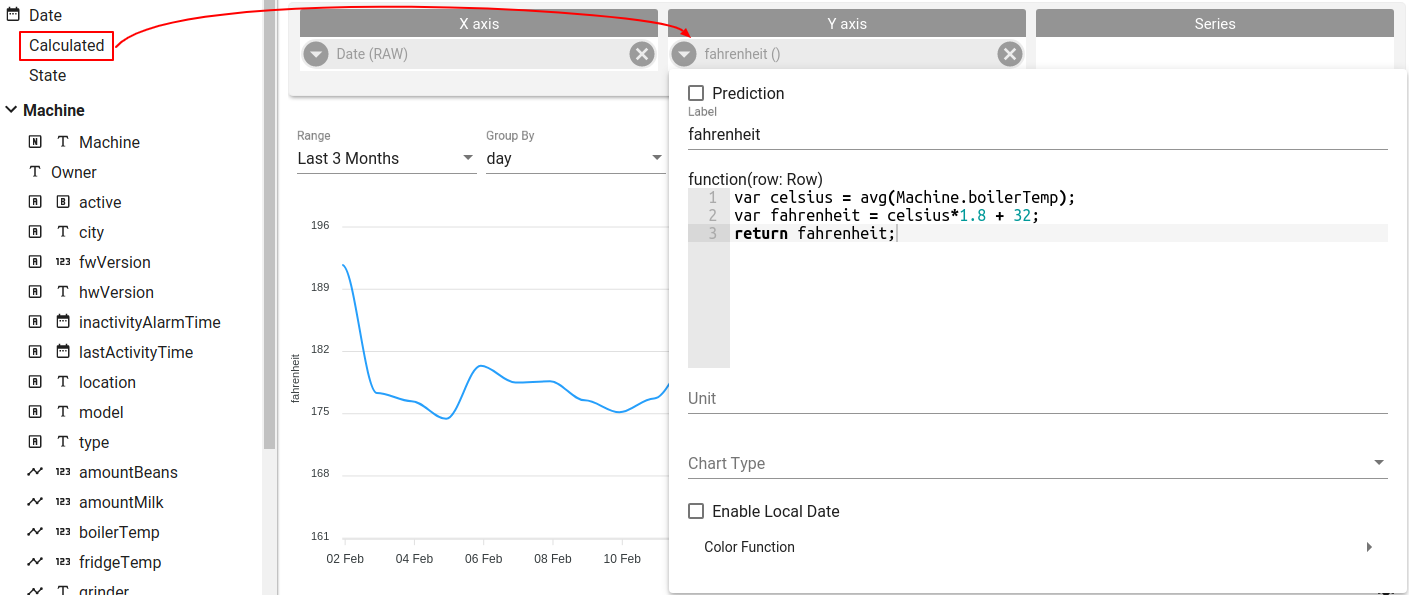
Simple calculation
Let’s assume that sensor submit boiler temperature in Celsius and we want convert it to Fahrenheit:
- Drop Calculated field from left navigation to the Y axis section
- Open field configration and write transformation function
1
2
3
var celsius = avg(Machine.boilerTemp);
var fahrenheit = celsius*1.8 + 32;
return fahrenheit;
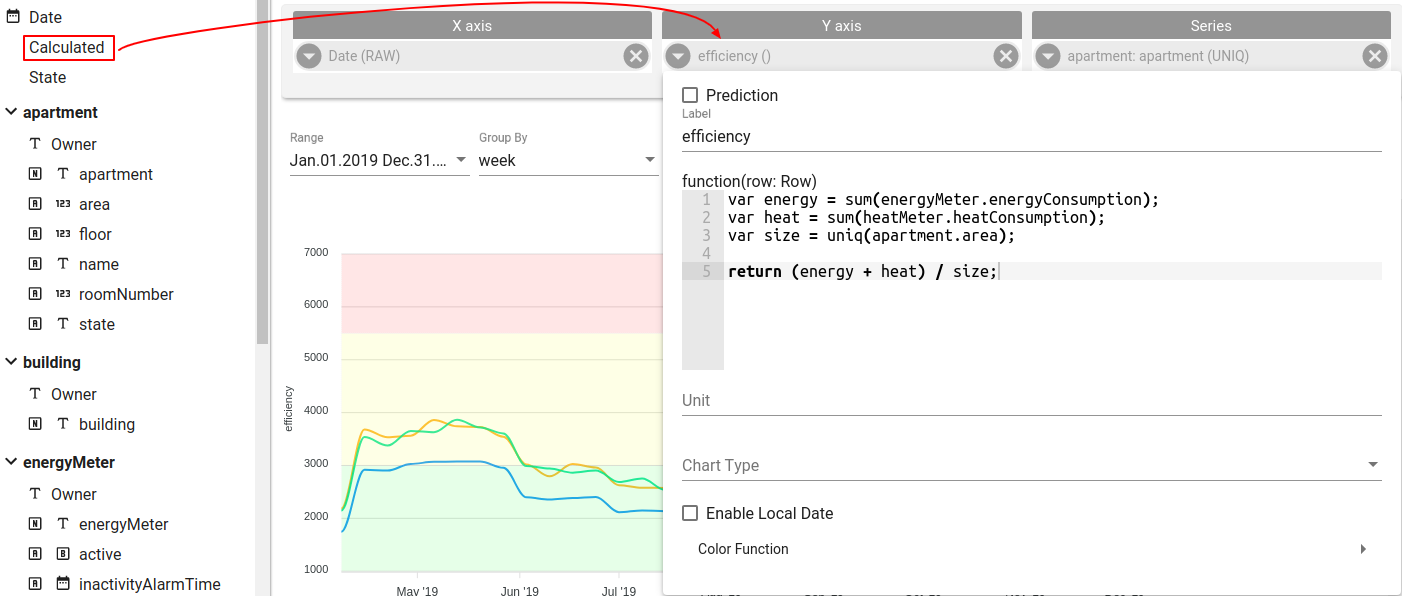
Multiple fields for calculation
In this example we have Apartment asset that has 2 sensors installed - HeatMeter and EnergyMeter. Both sensors submit how much energy was consumed. Also Apartment has area attribute that contains apartment size. We want calculate total energy consumed by HeatMeter and EnergyMeter in Apartment per square meter. Let’s break it to subtasks:
- Get amount of energy consumed by HeatMeter - heatConsumption telemetry
- Get amount of energy consumed by EnergyMeter - energyConsumption telemetry
- Get Appartment size - area attribute
- Sum heatConsumption and energyConsumption
- Devide it by area
For implementing this we need to:
- Drop Calculated field from left navigation to the Y axis section
- Open field configration and write transformation function
1
2
3
4
5
var energy = sum(energyMeter.energyConsumption);
var heat = sum(heatMeter.heatConsumption);
var size = uniq(apartment.area);
return (energy + heat) / size;
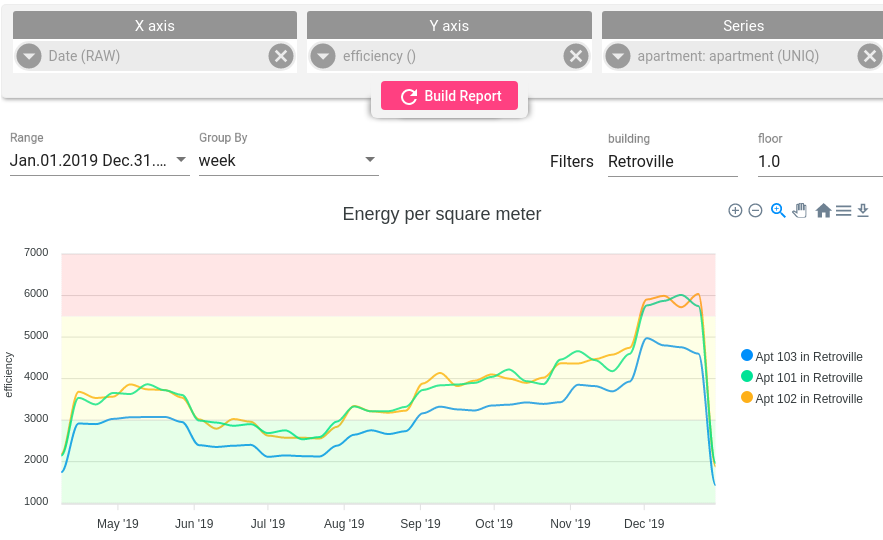
Get original field value
Before applying transformation you need to get a reference to the original field value. Here is an example how to do this:
1
var temp = avg(Machine.temperature);
- avg() - aggregation function
- Machine - Entity Name (it can be Asset Type or Device Type)
- temperature - Field Name
All 3 parts are required, you can not access original field value without aggregation function.
If original field value is an attribute, entity name or owner name - you should use uniq() aggregation function.
Supported Aggregation Functions
JSEditor for calculated fields supports following aggregation functions:
- avg()
- sum()
- min()
- max()
- count()
- latest()
- uniq()
- delta()
Each function allows only 1 argument - reference to the filed on format EntityName.fieldName. For example:
1
sum(Machine.temperature)
Aggregation function applied to a grouped dataset. Find more details about Grouping and Aggregation in this article
Batch calculation
When batch calculation option is disabled - you write a function that works with 1 value at a time. But when a batch
calculation is enabled you work with the whole raw telemetry array. With the enabled Batch calculation checkbox, you
receive more control over how raw telemetry is converted into the required metric. For example you can write a function that
has access to the previous telemetry value, you can filter or exclude telemetry value from calculation if needed, you can group telemetries by timestamp and apply transformation on group.
Once raw telemetry array was transformed and returned from the calculation function, system will apply required aggregation on that array.
Basic syntax
Let’s assume that you create following variable for telemetry data:
1
var temperatureReadings = none(thermostat.temperature);
In this case temperatureReadings variable would be an array of telemetry objects:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[
{
"ts": 1622505600000,
"value": 17
},
{
"ts": 1622592000000,
"value": 21
},
{
"ts": 1622678400000,
"value": 35
}
]
In case of attributes you also has an array with 1 object that represent an attribute. Here is an example how to use attributes insude your script:
1
2
3
4
var unit = uniq(thermostat.measureUnit);
if(unit.length) {
unit = unit[0].value;
}
Filter raw telemetry
You can exclude some telemetry values from metric calculation. In this example we will exclude all temperature values that bigger than 40:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
var temperatureReadings = none(thermostat.temperature);
var filteredReadings = [];
for (var i = 0; i < temperatureReadings.length; i++) {
var tsValue = temperatureReadings[i];
if(tsValue.value <= 40) {
filteredReadings.push(tsValue);
}
}
return filteredReadings;
Modify raw telemetry
Here is an example how to transform raw telemetry array based on attribute value:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
var temperatureReadings = none(thermostat.temperature);
var unit = uniq(thermostat.measureUnit);
if(unit.length) {
unit = unit[0].value;
}
for (var i = 0; i < temperatureReadings.length; i++) {
var tsValue = temperatureReadings[i];
if(unit === 'Fahrenheit') {
tsValue.value = 5 / 9 * (tsValue.value - 32);
}
}
return temperatureReadings;
Group multiple telemetries by timestamp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
var voltageTelemetry = none(energyMeter.voltage);
var temperatureTelemetry = none(energyMeter.temperature);
var pressureTelemetry = none(energyMeter.pressure);
var groupedTelemetry = {};
groupTelemetryByTime(voltageTelemetry, groupedTelemetry, 'voltage');
groupTelemetryByTime(temperatureTelemetry, groupedTelemetry, 'temperature');
groupTelemetryByTime(pressureTelemetry, groupedTelemetry, 'pressure');
// ... execute transformation
groupTelemetryByTime = function (telemetry, groupedTelemetry, keyName) {
for (var i = 0; i < telemetry.length; i++) {
var ts = telemetry[i].ts;
if(!groupedTelemetry[ts]) {
groupedTelemetry[ts] = {ts: ts};
}
groupedTelemetry[ts][keyName] = telemetry[i].value;
}
};
Fill gaps in telemetry stream
In this example we demonstrate how to detect gaps im timeseries stream and fill it with 0 values:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
var temperatureReadings = none(thermostat.temperature);
var timeGap = 30 * 60 * 1000; // 30 minutes
for (var i = 1; i < temperatureReadings.length; i++) {
var tsDelta = temperatureReadings[i].ts - temperatureReadings[i - 1].ts;
if (tsDelta > timeGap) {
var newTs = (temperatureReadings[i].ts + temperatureReadings[i - 1].ts) / 2;
temperatureReadings.splice(i, 0, {ts: newTs, value: 0})
}
}
return temperatureReadings;
Save and reuse calculated fields
Once the calculated field is created you can save it for future reuse by pressing Save Field button under function editor. Current field label would be used as a field name. If a field with such name already exists - the system will overwrite it.
Saved calculated field is only a template. Once it is dropped from the left navigation tree into some axis, a new calculated field created and this field would not be connected with the original template. It means that if you will update field configuration in the future, it will only update a template, but real calculated fields that are added to View configuration are not affected.
Language
Calculated Fields use Javascript as a language for writing transformation function. Inner Engine provide 100% support of ECMAScript 5.1
Next Steps
-
Getting started guide - These guide provide quick overview of main Trendz features.
-
Installation guides - Learn how to setup ThingsBoard on various available operating systems.
-
States - Learn how to define and analyse states for assets based on raw telemetry.
-
Group and Aggregate data - Learn how to group and aggregate data in Trendz.
-
Prediction - Learn how to make forecasts and predict telemetry behavior.
-
Filters - Learn how filter dataset during analysis.
-
Available Visualizations - Learn about visualization widgets available in Trendz and how to configure them.
-
Share and embed Visualizations - Learn how to add Trendz visualizations on ThingsBoard dashboard or 3rd party web pages.

