This guide will help you to get familiar with MQTT Connector configuration for ThingsBoard IoT Gateway. Use general configuration to enable this Connector. The purpose of this Connector is to connect to external MQTT broker and subscribe to data feed from devices. Connector is also able to push data to MQTT brokers based on the updates/commands from ThingsBoard.
This Connector is useful when you have local MQTT broker in your facility or corporate network and you would like to push data from this broker to ThingsBoard.
We will describe connector configuration file below.
Connector configuration: mqtt.json
Connector configuration is a JSON file that contains information about how to connect to external MQTT broker, what topics to use when subscribing to data feed and how to process the data. Let’s review the format of the configuration file using example below.
Example of MQTT Connector config file. Press to expand.
Example listed below will connect to MQTT broker in a local network deployed on server with IP 192.168.1.100. Connector will use basic MQTT auth using username and password. Then, connector will subscribe to a list of topics using topic filters from mapping section. See more info in a description below.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
{
"broker": {
"name":"Default Local Broker",
"host":"192.168.1.100",
"port":1883,
"security": {
"type": "basic",
"username": "user",
"password": "password"
}
},
"mapping": [
{
"topicFilter": "/sensor/data",
"converter": {
"type": "json",
"deviceNameJsonExpression": "${serialNumber}",
"deviceTypeJsonExpression": "${sensorType}",
"timeout": 60000,
"attributes": [
{
"type": "string",
"key": "model",
"value": "${sensorModel}"
},
{
"type": "string",
"key": "${sensorModel}",
"value": "on"
}
],
"timeseries": [
{
"type": "double",
"key": "temperature",
"value": "${temp}"
},
{
"type": "double",
"key": "humidity",
"value": "${hum}"
},
{
"type": "string",
"key": "combine",
"value": "${hum}:${temp}"
}
]
}
},
{
"topicFilter": "/sensor/+/data",
"converter": {
"type": "json",
"deviceNameTopicExpression": "(?<=sensor\/)(.*?)(?=\/data)",
"deviceTypeTopicExpression": "Thermometer",
"timeout": 60000,
"attributes": [
{
"type": "string",
"key": "model",
"value": "${sensorModel}"
}
],
"timeseries": [
{
"type": "double",
"key": "temperature",
"value": "${temp}"
},
{
"type": "double",
"key": "humidity",
"value": "${hum}"
}
]
}
},
{
"topicFilter": "/sensor/raw_data",
"converter": {
"type": "bytes",
"deviceNameExpression": "[0:4]",
"deviceTypeExpression": "default",
"timeout": 60000,
"attributes": [
{
"type": "raw",
"key": "rawData",
"value": "[:]"
}
],
"timeseries": [
{
"type": "raw",
"key": "temp",
"value": "[4:]"
}
]
}
},
{
"topicFilter": "/custom/sensors/+",
"converter": {
"type": "custom",
"extension": "CustomMqttUplinkConverter",
"extension-config": {
"temperatureBytes" : 2,
"humidityBytes" : 2,
"batteryLevelBytes" : 1
}
}
}
],
"connectRequests": [
{
"topicFilter": "/sensor/connect",
"deviceNameJsonExpression": "${serialNumber}"
},
{
"topicFilter": "/sensor/+/connect",
"deviceNameTopicExpression": "(?<=sensor\/)(.*?)(?=\/connect)"
}
],
"disconnectRequests": [
{
"topicFilter": "/sensor/disconnect",
"deviceNameJsonExpression": "${serialNumber}"
},
{
"topicFilter": "/sensor/+/disconnect",
"deviceNameTopicExpression": "(?<=sensor\/)(.*?)(?=\/disconnect)"
}
],
"attributeRequests": [
{
"retain": false,
"topicFilter": "v1/devices/me/attributes/request",
"topicExpression": "${SerialNumber}",
"valueExpression": "${sensorModel}"
}
],
"attributeUpdates": [
{
"retain": false,
"deviceNameFilter": "SN.*",
"attributeFilter": "uploadFrequency",
"topicExpression": "sensor/${deviceName}/${attributeKey}",
"valueExpression": "{\"${attributeKey}\":\"${attributeValue}\"}"
}
],
"serverSideRpc": [
{
"deviceNameFilter": "SN.*",
"methodFilter": "echo",
"requestTopicExpression": "/sensor/${deviceName}/request/${methodName}/${requestId}",
"responseTopicExpression": "/sensor/${deviceName}/response/${methodName}/${requestId}",
"responseTimeout": 10000,
"valueExpression": "${params}"
},
{
"deviceNameFilter": ".*",
"methodFilter": "no-reply",
"requestTopicExpression": "/sensor/${deviceName}/request/${methodName}/${requestId}",
"valueExpression": "${params.hum}::${params.temp}"
}
]
}
Section “broker”
| 参数 | Default value | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| name | Default Local Broker | Broker name for logs and saving to persistent devices. |
| host | localhost | Mqtt broker hostname or ip address. |
| port | 1883 | Mqtt port on the broker. |
| clientId | ThingsBoard_gateway | This is the client ID. It must be unique for each session. |
| version | 5 | MQTT protocol version. |
Subsection “security”
Subsection “security” provides configuration for client authorization at Mqtt Broker.
|
One type of security configuration is basic, For authorization will be used combination of username/password, provided in this section in config.
Security subsection in configuration file will look like this: |
|
Anonymous auth is the most simple option. It is useful for testing on public MQTT brokers, like test.mosquitto.org.
Security subsection in configuration file will look like this: |
|
In table below described parameters to configure authorization on mqtt broker .
Security subsection in configuration file will look like this: |
Section “mapping”
This configuration section contains array of topics that the gateway will subscribe to after connecting to the broker and settings about processing incoming messages (converter).
| Parameter | Default value | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| topicFilter | /sensor/data | Topic address for subscribing. |
The topicFilter supports special symbols: ‘#’ and ‘+’ to allow to subscribe to multiple topics.
Let’s assume we would like to subscribe and process following data from Thermometer devices:
| Example Name | Topic | Topic Filter | Payload | Comments |
| Example 1 | /sensor/data | /sensor/data | {"serialNumber": "SN-001", "sensorType": "Thermometer", "sensorModel": "T1000", "temp": 42, "hum": 58} | Device Name is part of the payload |
| Example 2 | /sensor/SN-001/data | /sensor/+/data | {"sensorType": "Thermometer", "sensorModel": "T1000", "temp": 42, "hum": 58} | Device Name is part of the topic |
In this case following messages are valid:
Example 1:
1
mosquitto_pub -h YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_HOST -p YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_PORT -t "/sensor/data" -m '{"serialNumber": "SN-001", "sensorType": "Thermometer", "sensorModel": "T1000", "temp": 42, "hum": 58}'
Example 2:
1
mosquitto_pub -h YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_HOST -p YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_PORT -t "/sensor/SN-001/data" -m '{"sensorType": "Thermometer", "sensorModel": "T1000", "temp": 42, "hum": 58}'
Now let’s review how we can configure JSON converter to parse this data
Subsection “converter”
This subsection contains configuration for processing incoming messages.
Types of mqtt converters:
- json – Default converter
- raw – Raw default converter
- custom – Custom converter (You can write it by yourself, and it will use to convert incoming data from the broker.)
|
Json converter is default converter, it looks for deviceName, deviceType, attributes and telemetry in the incoming message from the broker, with rules, described in this subsection:
Note: The device profile is set when the device is created. Changing the device profile using a Gateway is not provided. Mapping subsection for Example 1 will look like: Mapping for Example 2 will look like: |
|
Bytes converter is default converter, it looks for deviceName, deviceType, attributes and telemetry in the incoming message from the broker, with rules, described in this subsection:
Note: The device profile is set when the device is created. Changing the device profile using a Gateway is not provided. Mapping subsection will look like: |
|
A custom converter is converter written for some device:
Converter subsection in the configuration will look like: |
Note: You can specify multiple mapping objects inside the array.
Also, you can combine values from MQTT message in attributes, telemetry and serverSideRpc section, for example:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
{
{
"topicFilter": "/sensor/data",
"converter": {
"type": "json",
"deviceNameJsonExpression": "${serialNumber}",
"deviceTypeJsonExpression": "${sensorType}",
"timeout": 60000,
"attributes": [],
"timeseries": [
{
"type": "double",
"key": "temperature",
"value": "${temp}"
},
{
"type": "double",
"key": "humidity",
"value": "${hum}"
},
{
"type": "string",
"key": "combine",
"value": "${hum}:${temp}"
}
]
}
}
}
Mapping process subscribes to the MQTT topics using topicFilter parameter of the mapping object. Each message that is published to this topic by other devices or applications is analyzed to extract device name, type and data (attributes and/or timeseries values). By default, gateway uses Json converter, but it is possible to provide custom converter. See examples in the source code.
Now let’s review an example of sending data from “SN-001” thermometer device.
Let’s assume MQTT broker is installed locally on your server.
Use terminal to simulate sending message from the device to the MQTT broker:
1
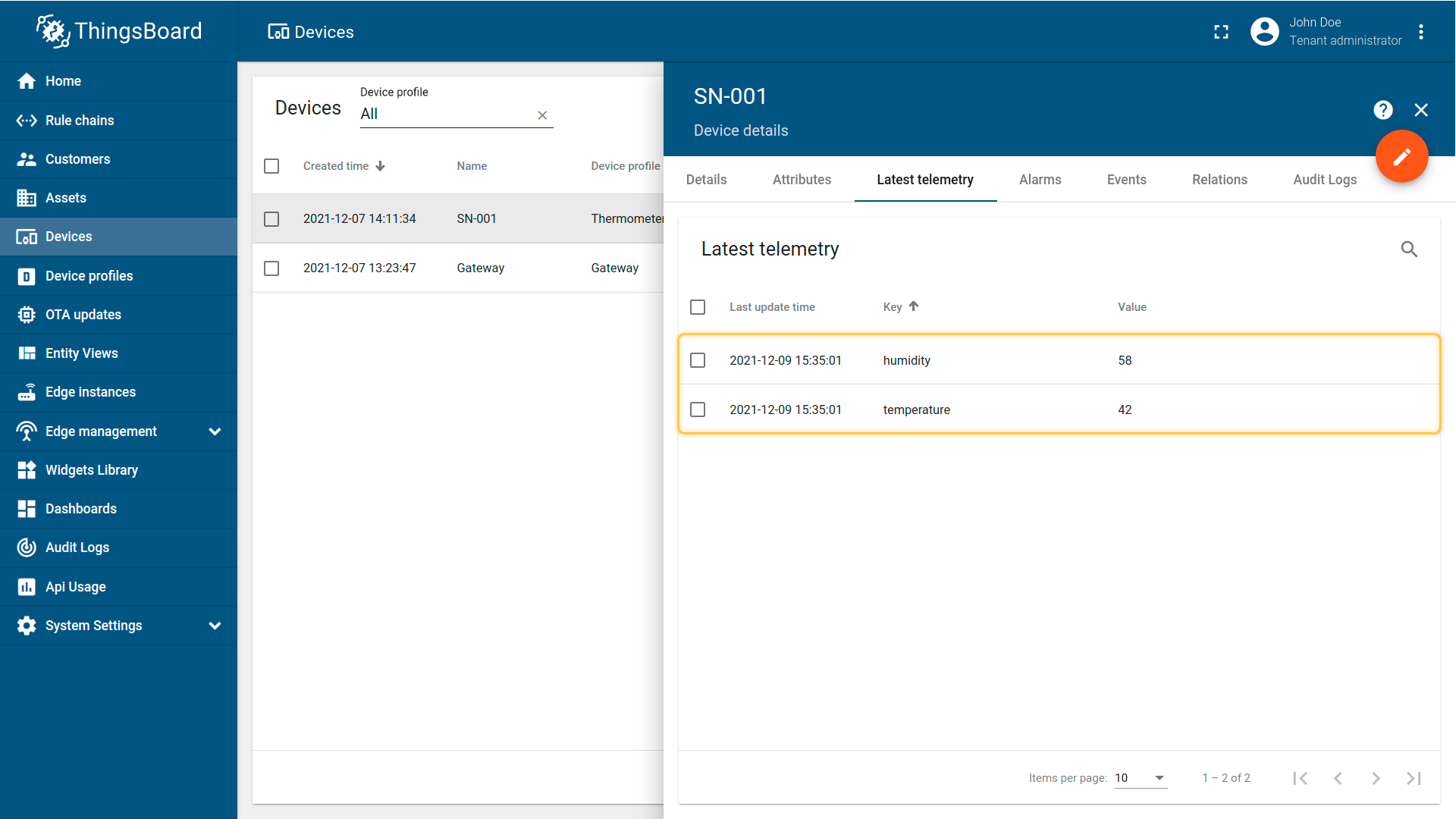
mosquitto_pub -h 127.0.0.1 -p 1883 -t "/sensor/data" -m '{"serialNumber": "SN-001", "sensorType": "Thermometer", "sensorModel": "T1000", "temp": 42, "hum": 58}'
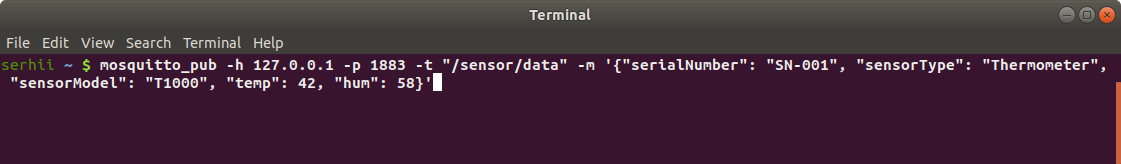
The device will be created and displayed in ThingsBoard based on the passed parameters.
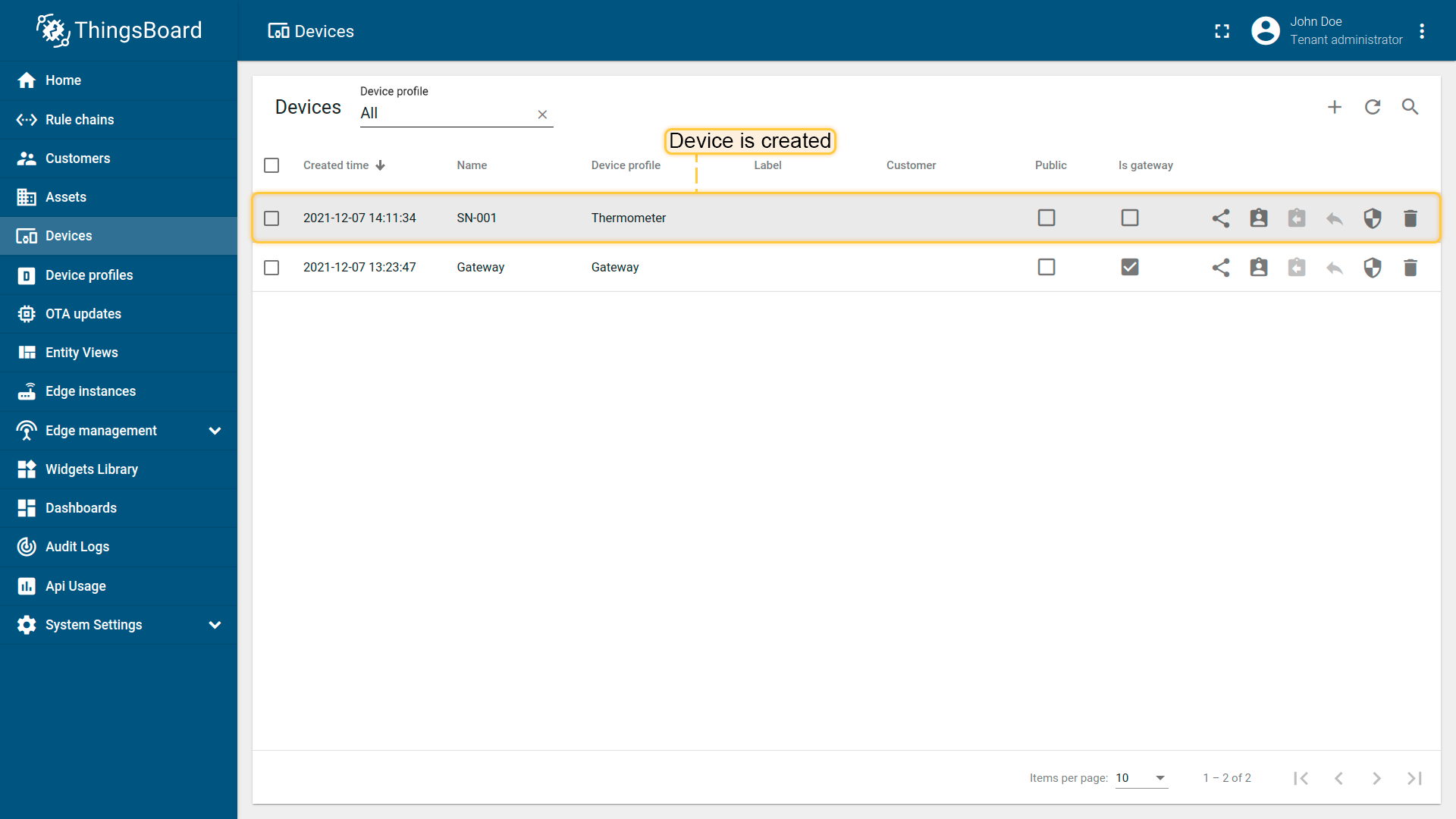
Section “connectRequests”
ThingsBoard allows sending RPC commands and notifications about device attribute updates to the device. But in order to send them, the platform needs to know if the target device is connected and what gateway or session is used to connect the device at the moment. If your device is constantly sending telemetry data - ThingsBoard already knows how to push notifications. If your device just connects to MQTT broker and waits for commands/updates, you need to send a message to the Gateway and inform that device is connected to the broker.
1. Name in a message from broker:
| 参数 | Default value | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| topicFilter | /sensor/connect | Topic address on the broker, where the broker sends information about new connected devices. |
| deviceNameJsonExpression | ${serialNumber} | JSON-path expression, for looking the new device name. |
2. Name in topic address:
| 参数 | Default value | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| topicFilter | /sensor/+/connect | Topic address on the broker, where the broker sends information about new connected devices. |
| deviceNameTopicExpression | (?<=sensor\/)(.*?)(?=\/connect) | Regular expression for looking the device name in topic path. |
This section in configuration looks like:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
"connectRequests": [
{
"topicFilter": "/sensor/connect",
"deviceNameJsonExpression": "${serialNumber}"
},
{
"topicFilter": "/sensor/+/connect",
"deviceNameTopicExpression": "(?<=sensor\/)(.*?)(?=\/connect)"
}
]
In this case following messages are valid:
1
mosquitto_pub -h YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_HOST -p YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_PORT -t "/sensor/connect" -m '{"serialNumber":"SN-001"}'
1
mosquitto_pub -h YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_HOST -p YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_PORT -t "/sensor/SN-001/connect" -m ''
Now let’s review an example.
Use a terminal to simulate sending a message from the device to the MQTT broker:
1
mosquitto_pub -h 127.0.0.1 -p 1883 -t "/sensor/connect" -m '{"serialNumber": "SN-001"}'
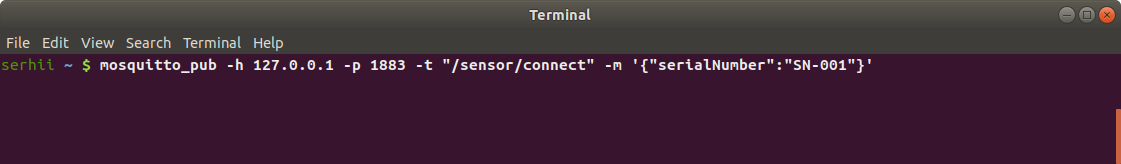
Your ThingsBoard instance will get information from the broker about last connecting time of the device. You can see this information on the “Server attributes” scope (“Attributes” tab).
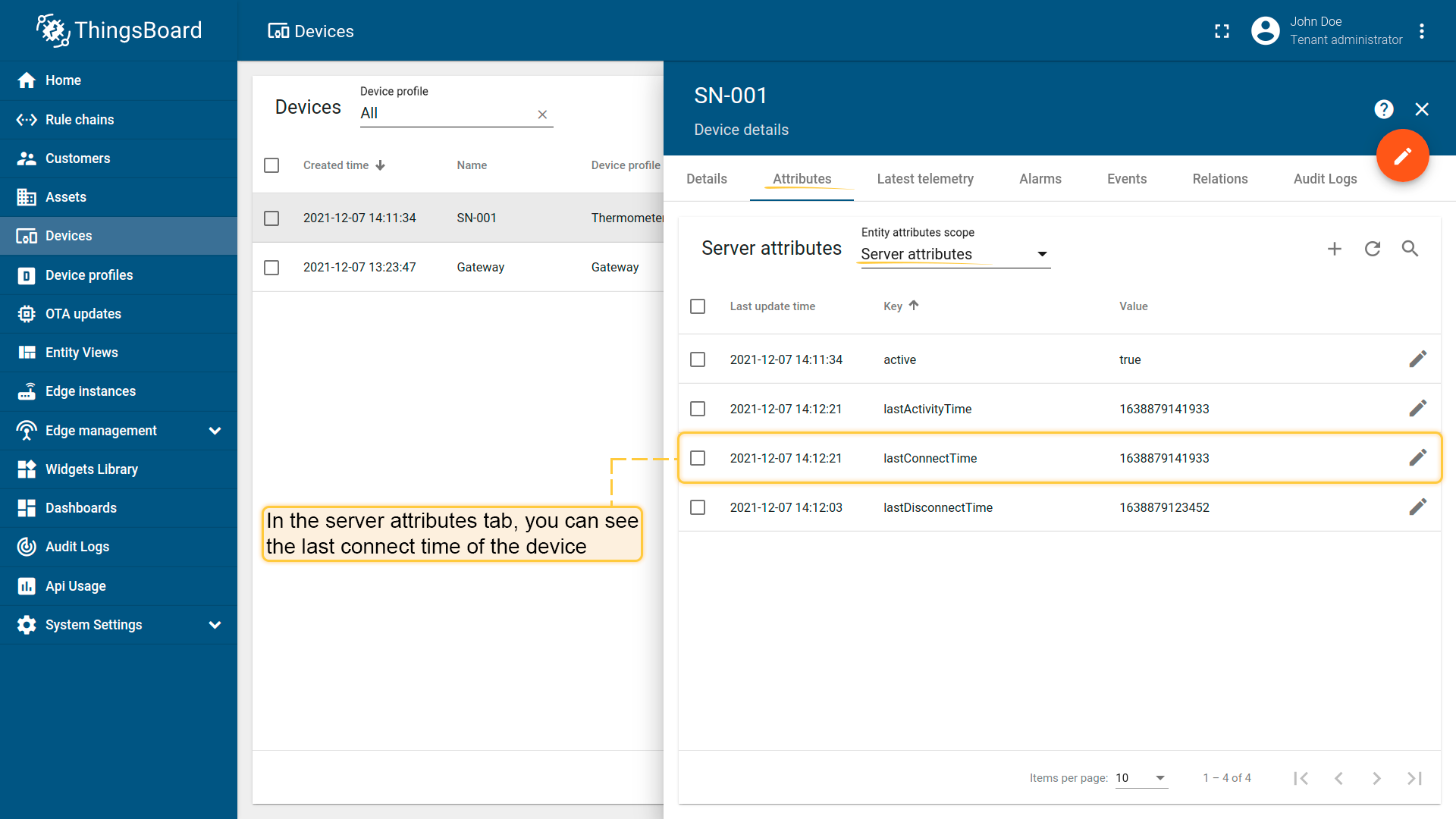
Section “disconnectRequest”
This configuration section is optional.
Configuration, provided in this section will be used to get information from the broker about disconnecting device.
If your device just disconnects from MQTT broker and waits for commands/updates, you need to send a message to the Gateway and inform that device is disconnected from the broker.
1. Name in a message from broker:
| 参数 | Default value | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| topicFilter | /sensor/disconnect | Topic address on the broker, where the broker sends information about disconnected devices. |
| deviceNameJsonExpression | ${serialNumber} | JSON-path expression, for looking the new device name. |
2. Name in topic address:
| 参数 | Default value | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| topicFilter | /sensor/+/disconnect | Topic address on the broker, where the broker sends information about disconnected devices. |
| deviceNameTopicExpression | (?<=sensor\/)(.*?)(?=\/connect) | Regular expression for looking the device name in topic path. |
This section in configuration file looks like:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
"disconnectRequests": [
{
"topicFilter": "/sensor/disconnect",
"deviceNameJsonExpression": "${serialNumber}"
},
{
"topicFilter": "/sensor/+/disconnect",
"deviceNameTopicExpression": "(?<=sensor\/)(.*?)(?=\/disconnect)"
}
]
In this case following messages are valid:
1
mosquitto_pub -h YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_HOST -p YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_PORT -t "/sensor/disconnect" -m '{"serialNumber":"SN-001"}'
1
mosquitto_pub -h YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_HOST -p YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_PORT -t "/sensor/SN-001/disconnect" -m ''
Now let’s review an example.
Use a terminal to simulate sending a message from the device to MQTT broker:
1
mosquitto_pub -h 127.0.0.1 -p 1883 -t "/sensor/disconnect" -m '{"serialNumber": "SN-001"}'
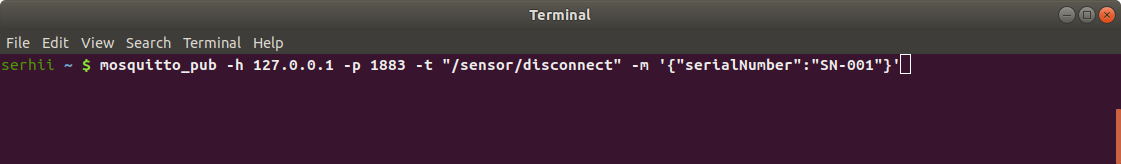
Your ThingsBoard instance will get information from the broker about last disconnecting time of the device. You can see this information on the “Server attributes” scope (“Attributes” tab).
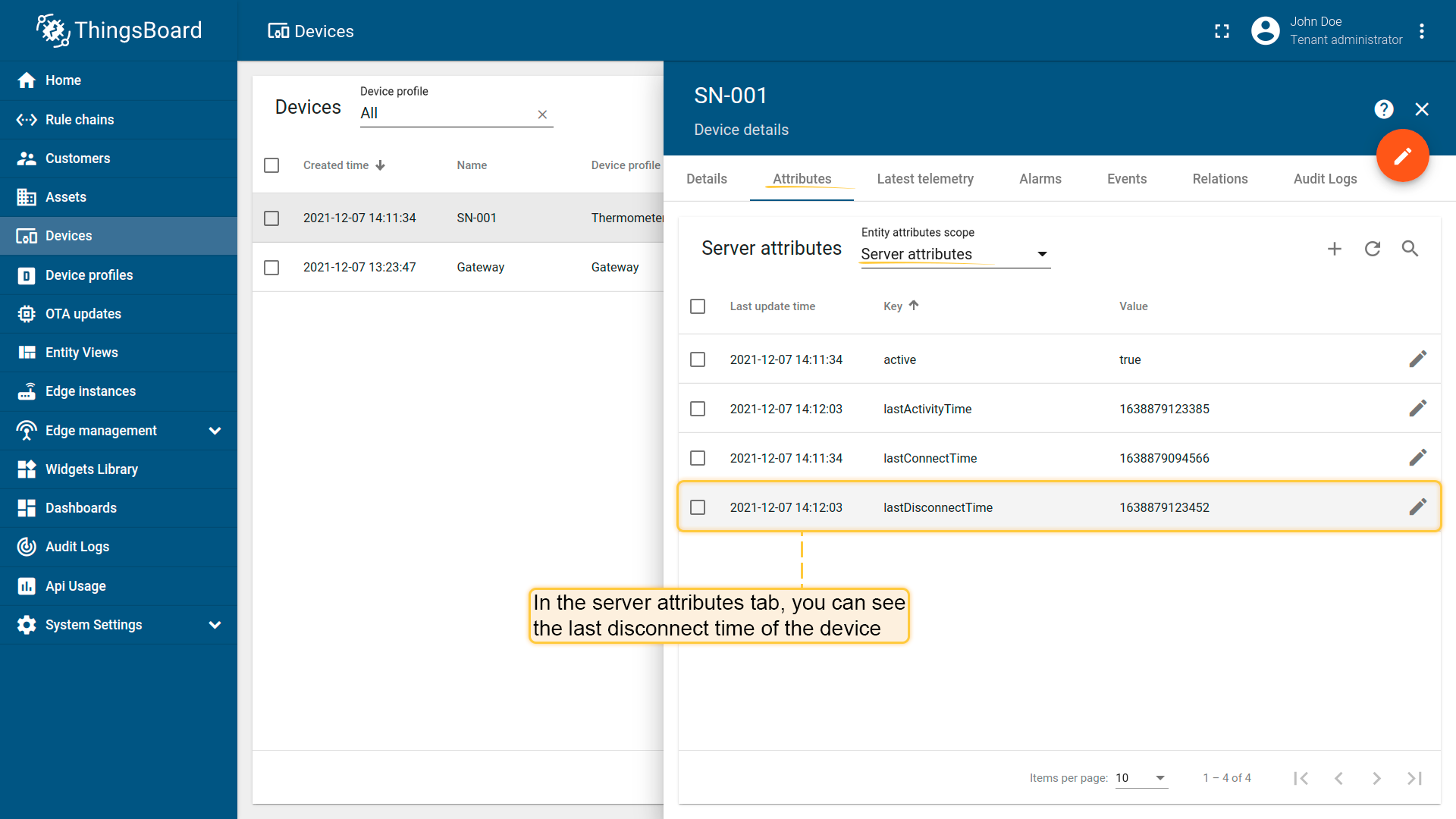
Section “attributeRequests”
Configuration in this section are optional.
In order to request client-side or shared device attributes to ThingsBoard server node, Gateway allows sending attribute requests.
| 参数 | Default value | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| retain | false | If set to true, the message will be set as the “last known good”/retained message for the topic. |
| topicFilter | v1/devices/me/attributes/request | Topic for attribute request |
| deviceNameJsonExpression | ${serialNumber} | JSON-path expression, for looking the device name in topicFilter message |
| attributeNameJsonExpression | ${versionAttribute} | JSON-path expression, for looking the attribute name in topicFilter message |
| topicExpression | devices/${deviceName}/attrs | JSON-path expression, for formatting reply topic |
| valueExpression | ${attributeKey}: ${attributeValue} | Message that will be sent to topic from topicExpression |
This section in configuration file looks like:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
"attributeRequests": [
{
"retain": false,
"topicFilter": "v1/devices/me/attributes/request",
"deviceNameJsonExpression": "${serialNumber}",
"attributeNameJsonExpression": "${versionAttribute}",
"topicExpression": "devices/${deviceName}/attrs",
"valueExpression": "${attributeKey}: ${attributeValue}"
}
]
Also, you can request multiple attributes at once. Simply add one more JSON-path to attributeNameExpression parameter. For example, we want to request two shared attributes in one request, our config will look like:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
"attributeRequests": [
{
"retain": false,
"topicFilter": "v1/devices/me/attributes/request",
"deviceNameJsonExpression": "${serialNumber}",
"attributeNameJsonExpression": "${versionAttribute}, ${pduAttribute}",
"topicExpression": "devices/${deviceName}/attrs",
"valueExpression": "${attributeKey}: ${attributeValue}"
}
]
Section “attributeUpdates”
This configuration section is optional.
ThingsBoard allows to provision device attributes and fetch some of them from the device application.
You can treat this as a remote configuration for devices. Your devices are able to request shared attributes from ThingsBoard.
See user guide for more details.
The “attributeRequests” configuration allows configuring the format of the corresponding attribute request and response messages.
| 参数 | Default value | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| retain | false | If set to true, the message will be set as the “last known good”/retained message for the topic |
| deviceNameFilter | SN.* | Regular expression device name filter, uses to determine, which function to execute. |
| attributeFilter | uploadFrequency | Regular expression attribute name filter, uses to determine, which function to execute. |
| topicExpression | /sensor/${deviceName}/${attributeKey} | JSON-path expression uses for creating topic address to send a message. |
| valueExpression | {\”${attributeKey}\”:\”${attributeValue}\”} | JSON-path expression uses for creating the message data that will send to topic. |
This section in configuration file looks like:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
"attributeUpdates": [
{
"retain": false,
"deviceNameFilter": "SN.*",
"attributeFilter": "uploadFrequency",
"topicExpression": "/sensor/${deviceName}/${attributeKey}",
"valueExpression": "{\"${attributeKey}\":\"${attributeValue}\"}"
}
]
Let’s look at an example.
Run the command below. You will start the mosquitto_sub client that subscribes to the topic “/sensor/SN-001/FirmwareVersion” of the local broker and start waiting for new messages from ThingsBoard server to broker.
1
mosquitto_sub -t /sensor/SN-001/FirmwareVersion
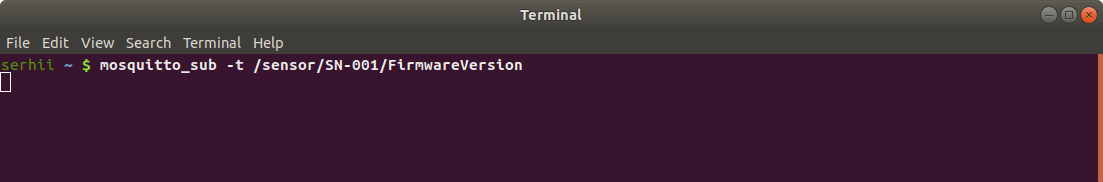
Update device attribute value on the ThingsBoard server. Open Devices -> click by your device -> Attributes tab -> Shared attributes scope and click on the “pencil” button next to “FirmwareVersion” attribute.
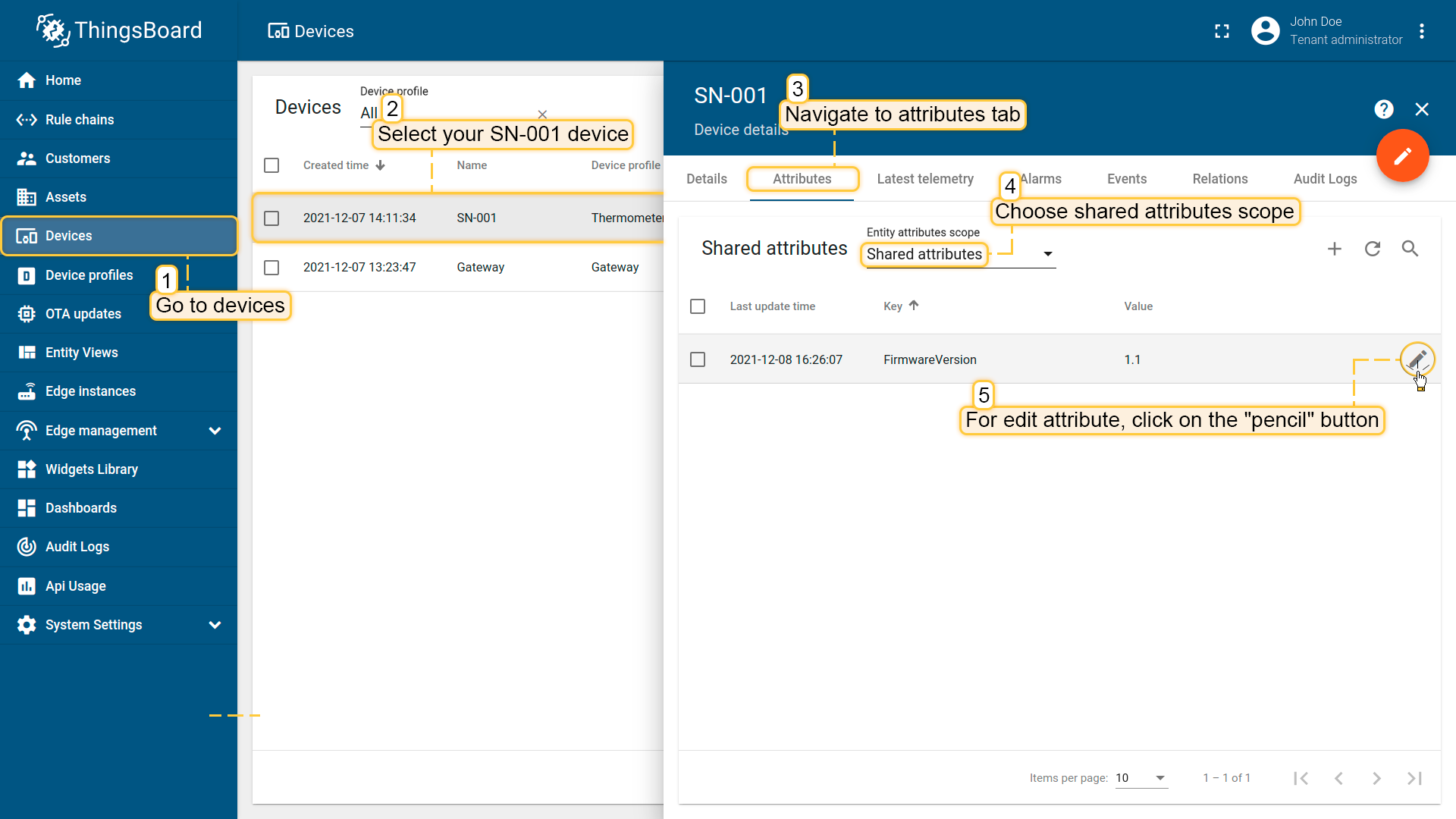
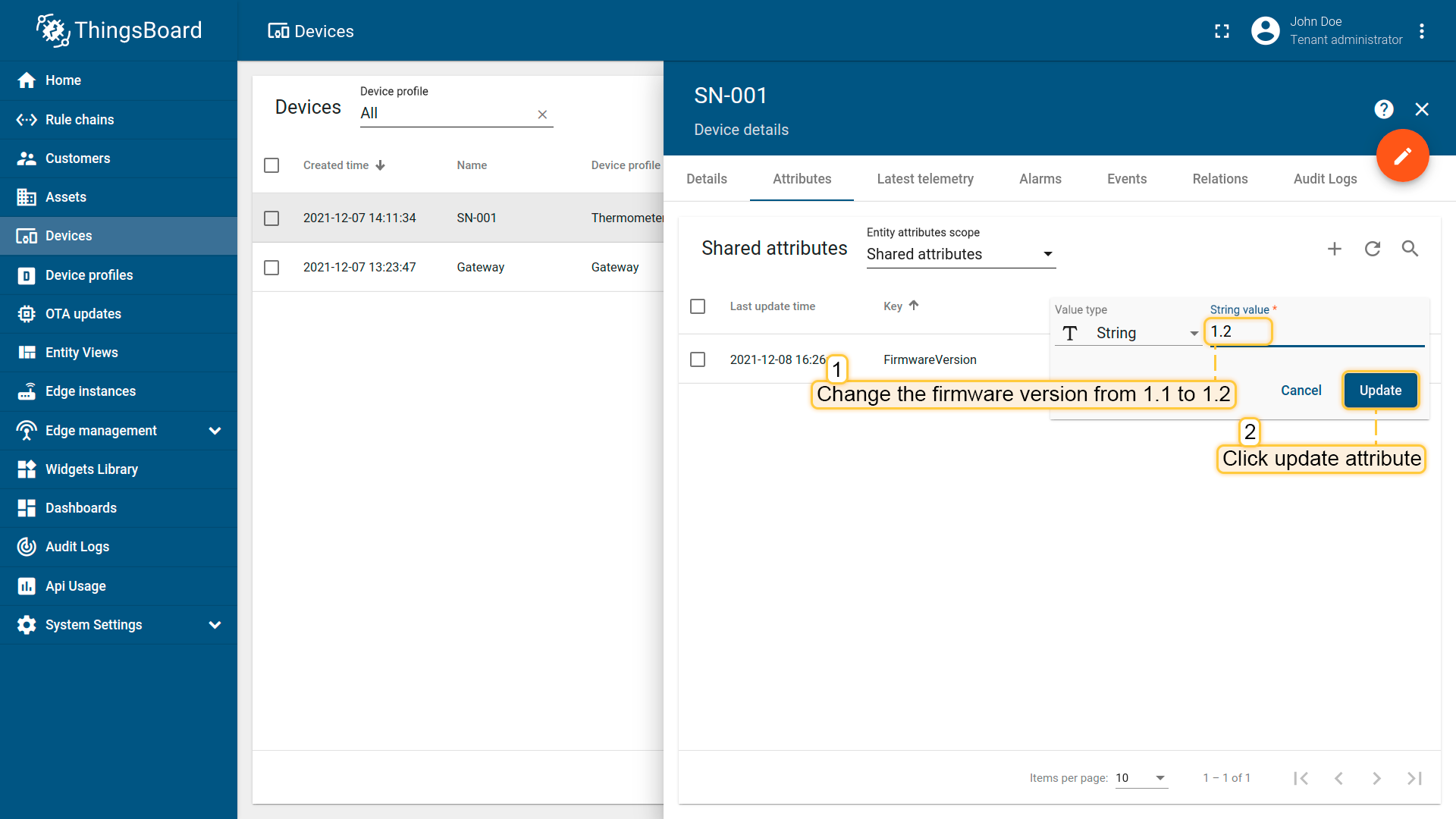
Change firmware version value from “1.1” to “1.2”. Then click “Update” button.
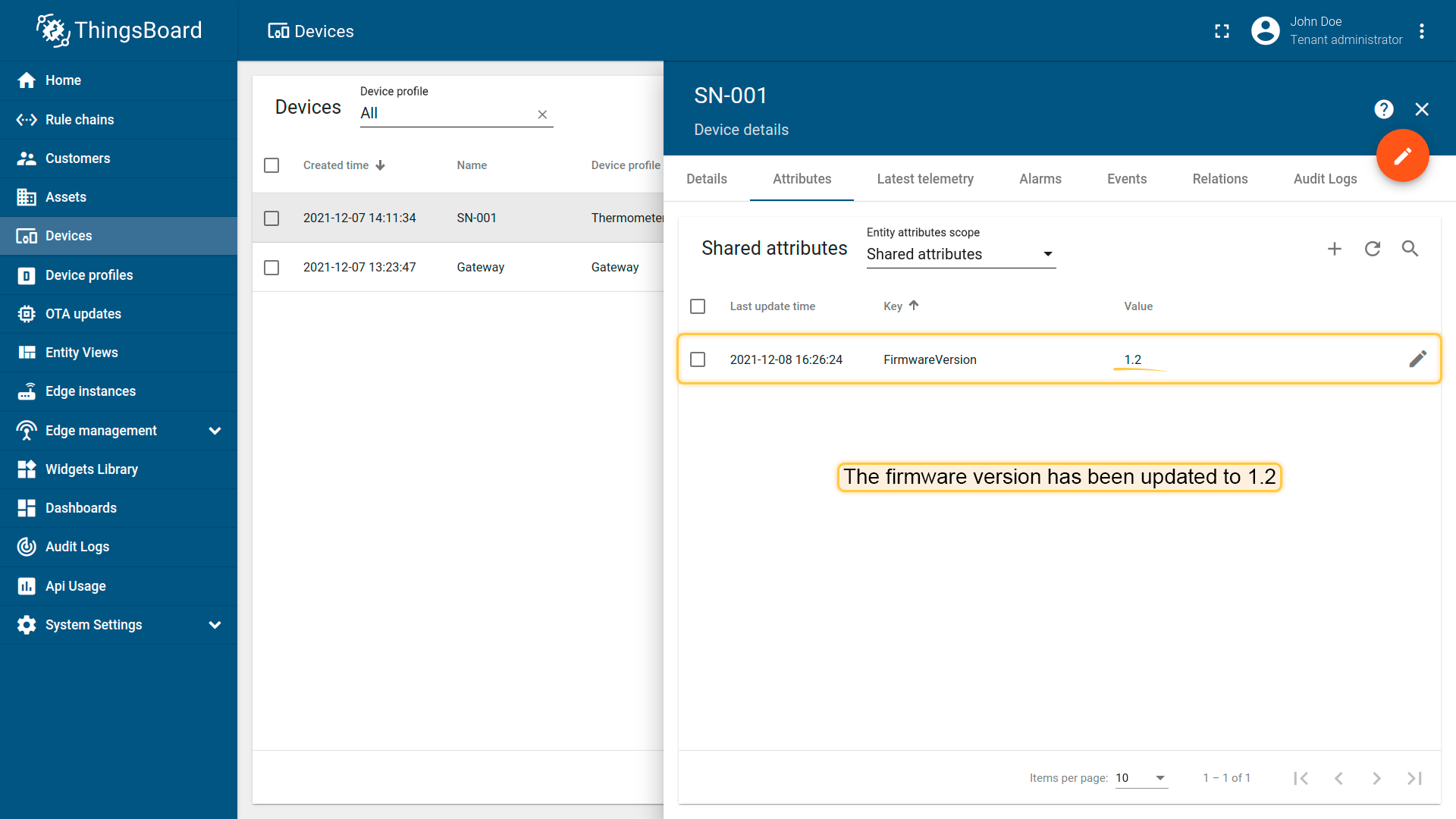
The firmware version has been updated to “1.2”.
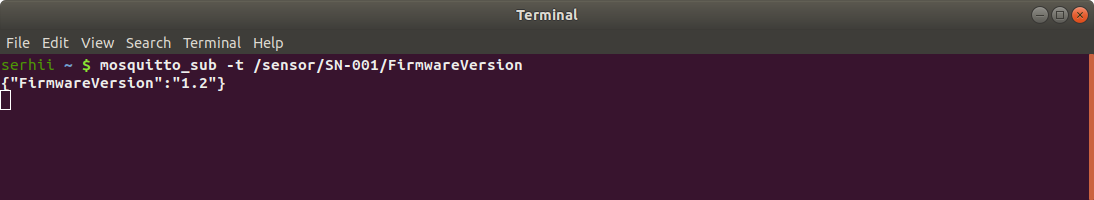
Broker received new message from the ThingsBoard server about updating attribute “FirmwareVersion” to “1.2”.
Server side RPC commands
ThingsBoard allows sending RPC commands to the device that is connected to ThingsBoard directly or via Gateway.
Configuration, provided in this section uses for sending RPC requests from ThingsBoard to device.
| 参数 | Default value | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| deviceNameFilter | SN.* | Regular expression device name filter, uses to determine, which function to execute. In the example configuration, we are using a filter for device name that starts with “SN”. |
| methodFilter | echo | Regular expression method name filter, uses to determine, which function to execute. |
| requestTopicExpression | /sensor/${deviceName}/request/${methodName}/${requestId} | JSON-path expression, uses for creating topic address to send RPC request. |
| responseTopicExpression | /sensor/${deviceName}/response/${methodName}/${requestId} | JSON-path expression, uses for creating topic address to subscribe for response message. |
| responseTimeout | 10000 | Value in milliseconds, if no response in this period after sending request, gateway will unsubscribe from response topic. |
| valueExpression | ${params} | JSON-path expression, uses for creating data for sending to broker. |
This section in configuration file looks like:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
"serverSideRpc": [
{
"deviceNameFilter": "SN.*",
"methodFilter": "echo",
"requestTopicExpression": "/sensor/${deviceName}/request/${methodName}/${requestId}",
"responseTopicExpression": "/sensor/${deviceName}/response/${methodName}/${requestId}",
"responseTimeout": 10000,
"valueExpression": "${params}"
},
{
"deviceNameFilter": ".*",
"methodFilter": "no-reply",
"requestTopicExpression": "/sensor/${deviceName}/request/${methodName}/${requestId}",
"valueExpression": "${params.hum}::${params.temp}"
}
]
As you can use deviceNameFilter and methodFilter to apply different mapping rules for different devices/methods. Once Gateway receives RPC request from the server to the device, it will publish the corresponding message based on requestTopicExpression and valueExpression. In case you expect the reply to the request from device, you should also specify responseTopicExpression and responseTimeout. The Gateway will subscribe to the “response” topic and wait for device reply until “responseTimeout” is detected (in milliseconds).
Example of RPC request (rpc-request.json) that need to be sent from the server:
1
2
3
4
5
6
{
"method": "echo",
"params": {
"message": "Hello!"
}
}
Also, every telemetry and attribute parameter has built-in GET and SET RPC methods out of the box, so you don’t need to configure it manually. To use them, make sure you set all required parameters (in the case of MQTT Connector, these are the following: requestTopicExpression, responseTopicExpression, responseTimeout, valueExpression). See the guide.
Next steps
Explore guides related to main ThingsBoard features:
- Data Visualization - how to visualize collected data.
- Device attributes - how to use device attributes.
- Telemetry data collection - how to collect telemetry data.
- Using RPC capabilities - how to send commands to/from devices.
- Rule Engine - how to use rule engine to analyze data from devices.

