- Overview
- Prerequisites
- Create Converter templates
- Create Integration template
- Modify Edge Root Rule chain for Downlinks
- Assign Integration to Edge
- Installing and running external UDP Integration
- Send uplink message
- Send downlink message
- Next steps
Overview
UDP Integration allows to stream data from devices which use a UDP transport protocol to ThingsBoard Edge and converts payloads of these devices into the ThingsBoard Edge format.
Please review the integration diagram to learn more.
Prerequisites
In this tutorial, we will use:
- ThingsBoard PE Edge;
- UDP Integration, running externally and connected to the ThingsBoard Edge instance;
- echo command which intended to display a line of text, and will redirect it’s output to netcat (nc) utility;
- netcat (nc) utility to establish UDP connections, receive data from there and transfer them;
Let’s assume that we have a sensor which is sending current temperature and humidity readings. Our sensor device SN-001 publishes it’s temperature and humidity readings to UDP Integration on 11560 port to the machine where UDP Integration is running.
For demo purposes we assume that our device is smart enough to send data in 3 different payload types:
- Text - in this case payload is SN-001,default,temperature,25.7,humidity,69
- JSON - in this case payload is
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
[
{
"deviceName": "SN-001",
"deviceType": "default",
"temperature": 25.7,
"humidity": 69
}
]
- Binary - in this case payload is: \x53\x4e\x2d\x30\x30\x31\x64\x65\x66\x61\x75\x6c\x74\x32\x35\x2e\x37\x36\x39 (in HEX string).
Here is the description of the bytes in this payload:
- 0-5 bytes - \x53\x4e\x2d\x30\x30\x31 - device name. If we convert it to text - SN-001;
- 6-12 bytes - \x64\x65\x66\x61\x75\x6c\x74 - device type. If we convert it to text - default;
- 13-16 bytes - \x32\x35\x2e\x37 - temperature telemetry. If we convert it to text - 25.7;
- 17-18 bytes - \x36\x39 - humidity telemetry. If we convert it to text - 69;
- Hex - in this case payload is hexadecimal string 534e2d30303164656661756c7432352e373639.
Here is the description of the bytes in this payload:
- 0-5 bytes - 534e2d303031 - device name. If we convert it to text - SN-001;
- 6-12 byte - 64656661756c74 - device type. If we convert it to text - default;
- 13-16 byte - 32352e37 - temperature telemetry. If we convert it to text: - 25.7;
- 17-18 byte - 3639 - humidity telemetry. If we convert it to text: - 69;
You can select payload type based on your device capabilities and business cases.
Create Converter templates
Converter and Integration templates are created on the Cloud, so please log in as Tenant administrator to cloud instance.
Uplink Converter template
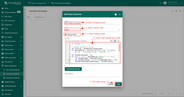
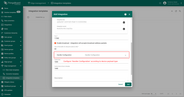
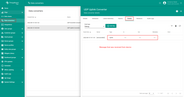
Before creating the Integration template, you need to create an Uplink and Downlink converter templates in Converters templates page. Uplink is necessary in order to convert the incoming data from the device into the required format for displaying them in ThingsBoard Edge. Click on the ‘plus’ and on ‘Create new converter’. To view the events, enable Debug. In the function decoder field, specify a script to parse and transform data.
Choose device payload type to for decoder configuration:
|
Now copy & paste the following script to the Decoder function section: The purpose of the decoder function is to parse the incoming data and metadata to a format that ThingsBoard can consume. deviceName and deviceType are required, while attributes and telemetry are optional. attributes and telemetry are flat key-value objects. Nested objects are not supported. |
|
Now copy & paste the following script to the Decoder function section: The purpose of the decoder function is to parse the incoming data and metadata to a format that ThingsBoard can consume. deviceName and deviceType are required, while attributes and telemetry are optional. attributes and telemetry are flat key-value objects. Nested objects are not supported. |
|
Now copy & paste the following script to the Decoder function section: The purpose of the decoder function is to parse the incoming data and metadata to a format that ThingsBoard can consume. deviceName and deviceType are required, while attributes and telemetry are optional. attributes and telemetry are flat key-value objects. Nested objects are not supported. |
|
Now copy & paste the following script to the Decoder function section: The purpose of the decoder function is to parse the incoming data and metadata to a format that ThingsBoard can consume. deviceName and deviceType are required, while attributes and telemetry are optional. attributes and telemetry are flat key-value objects. Nested objects are not supported. |
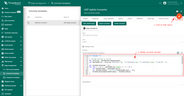
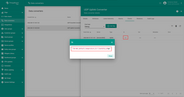
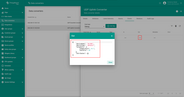
You can change the decoder function while creating the converter or after creating it. If the converter has already been created, then click on the ‘pencil’ icon to edit it. Copy the configuration example for the converter (or your own configuration) and insert it into the decoder function. Save changes by clicking on the ‘checkmark’ icon.
Downlink Converter template
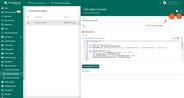
Create Downlink in Converter templates page as well. To see events select Debug checkbox.
You can customize a downlink according to your configuration. Let’s consider an example where we send an attribute update message. An example of downlink converter:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// Encode downlink data from incoming Rule Engine message
// msg - JSON message payload downlink message json
// msgType - type of message, for ex. 'ATTRIBUTES_UPDATED', 'POST_TELEMETRY_REQUEST', etc.
// metadata - list of key-value pairs with additional data about the message
// integrationMetadata - list of key-value pairs with additional data defined in Integration executing this converter
var result = {
// downlink data content type: JSON, TEXT or BINARY (base64 format)
contentType: "JSON",
// downlink data
data: JSON.stringify(msg),
// Optional metadata object presented in key/value format
metadata: {
}
};
return result;
Create Integration template
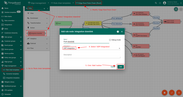
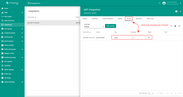
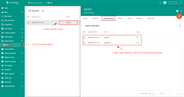
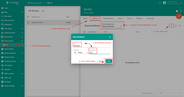
Now that the Uplink and Downlink converter templates have been created, it is possible to create an integration. Go to Integration templates section and click Add new integration button. Name it UDP Integration, select type UDP, turn the Debug mode on and from drop-down menus add recently created Uplink and Downlink converters.
As you mentioned Execute remotely is checked and can not be modified - UDP Integration can be only remote type.
Please note down Integration key and Integration secret - we will use these values later in the configuration on the remote UDP Integration itself.
By default UDP Integration will use 11560 port, but you can change this to any available port in your case.
We leave other options by default, but there is brief description of them:
- Enable broadcast - integration will accepts broadcast address packets - a flag indicating that integration will accept UDP packets that were sent to broadcast address;
- Size of the buffer for inbound socket - the size in KBytes of the socket data receive buffer;
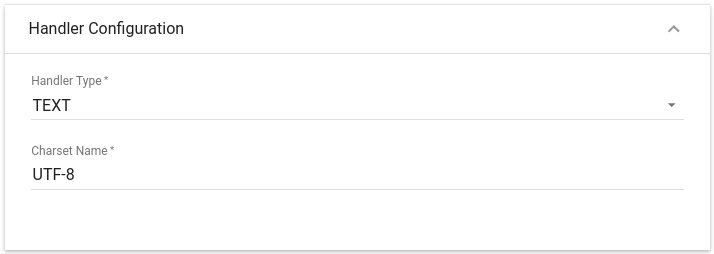
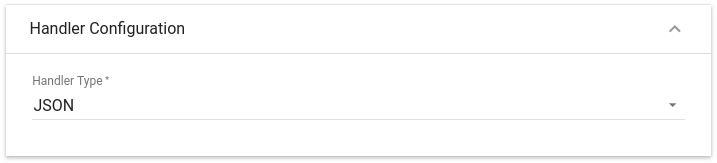
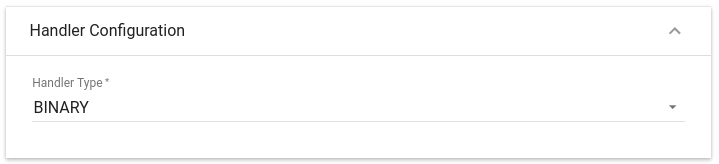
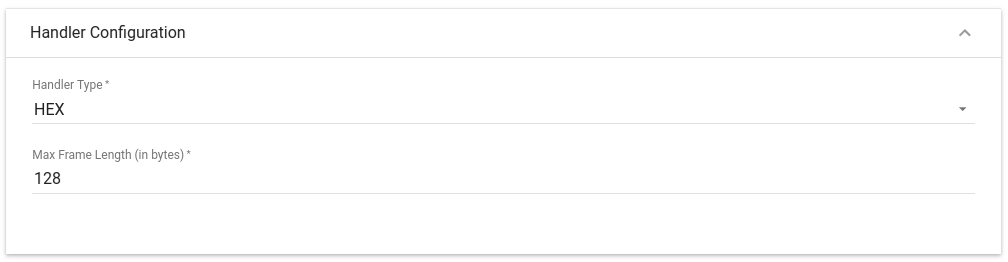
Choose device payload type for Handler Configuration:
|
Please select Handler Type as TEXT
To parse payload properly, please make sure that next values are set:
|
|
Please select Handler Type as JSON
|
|
Please select Handler Type as BINARY
|
|
Please select Handler Type as HEX
|
Click Add to save the Integration.
Modify Edge Root Rule chain for Downlinks
We can send a downlink message to the device from Rule chain using the rule node. To be able to send downlink over integration we need to modify ‘Edge Root Rule chain’ on the cloud. For example, create an integration downlink node and set the ‘Attributes updated’ link to it. When changes are made to device attribute, the downlink message will be sent to the integration.
Assign Integration to Edge
Once converter and integration templates are created, we can assign Integration template to Edge.
- Click Manage Integrations button of Edge entity
- Assign Integration to the Edge
- Login to your ThingsBoard PE Edge instance and open Integrations page
Installing and running external UDP Integration
Please refer to the Remote Integration guide and install UDP Integration service locally or on separate machine.
Please use Integration key and Integration secret from the above section for your UDP Integration configuration.
Send uplink message
Once ThingsBoard UDP Integration has been created, the UDP server starts, and then it waits for data from the devices.
Choose device payload type to send uplink message:
|
The command to send a message to the UDP server that is running on localhost (127.0.0.1) will look like this: |
|
The command to send a message to the UDP server that is running on localhost (127.0.0.1) will look like this: |
|
The command to send a message to the UDP server that is running on localhost (127.0.0.1) will look like this: |
|
The command to send a message to the UDP server that is running on localhost (127.0.0.1) will look like this: |
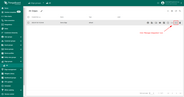
The created device with data can be seen in the section Device groups -> All on the Edge:
Received data can be viewed in the Uplink converter. In the ‘In’ and ‘Out’ blocks of the Events tab:
Send downlink message
Now let’s check downlink functionality.
Now we’ll need to send again message to UDP integration to see downlink response. Please use the same command that was used before, but replace parameter q1 to q120. With these changes nc utility will wait 120 seconds for downlink message. Additionally, please remove w1 parameter.
After you’ll send uplink command, you have 120 seconds to add firmware shared attribute:
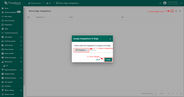
To make sure that downlink message sent to integration you can check ‘Events’ tab of integration:
An example of sent message and a response from ThingsBoard Edge in the terminal:
Next steps
-
Getting started guide - Provide quick overview of main ThingsBoard Edge features. Designed to be completed in 15-30 minutes:
-
Installation guides - Learn how to setup ThingsBoard Edge on various available operating systems and connect to ThingsBoard CE server.
-
Edge Rule Engine:
-
Overview - Learn about ThingsBoard Edge Rule Engine.
-
Rule Chain Templates - Learn how to use ThingsBoard Edge Rule Chain Templates.
-
Provision Rule Chains from cloud to edge - Learn how to provision edge rule chains from cloud to edge.
-
Push data from edge to cloud and vice versa - Learn how to push data from edge to cloud and vice versa.
-
- Security:
- gRPC over SSL/TLS - Learn how to configure gRPC over SSL/TLS for communication between edge and cloud.
-
Features:
-
Edge Status - Learn about Edge Status page on ThingsBoard Edge.
-
Cloud Events - Learn about Cloud Events page on ThingsBoard Edge.
-
-
Use cases:
-
Manage alarms and RPC requests on edge devices - This guide will show how to generate local alarms on the edge and send RPC requests to devices connected to edge:
-
Data filtering and traffic reduce - This guide will show how to send to cloud from edge only filterd amount of device data:
-
- Roadmap - ThingsBoard Edge roadmap.